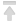8.2.26 Installation and Configuration of Mailcow on the Server

Mailcow is a self-hosted mail server suite built around Docker containers. It is for those who are tired of trusting their correspondence to “big friendly corporations” and want to keep emails under their own control.
Key features:
- Containerization: everything runs in Docker, each service is isolated (Postfix, Dovecot, Rspamd, ClamAV, MariaDB, Redis, etc.).
- Web interface: a convenient admin panel on PHP/NGINX for managing domains, mailboxes, aliases, and antispam.
- Security: built-in DKIM, SPF, DMARC, TLS support, automatic certificate renewal via ACME/Let’s Encrypt.
- Antispam/antivirus: email filtering through Rspamd and ClamAV.
- Flexibility: support for SOGo (web calendar, contacts, webmail), API for integration, extensibility by configuring services.
Server preparation
Requirements
- A virtual or dedicated server.
- Open incoming TCP ports: 25, 80, 443, 110, 143, 465, 587, 993, 995, 4190.
- An active domain name for
MAILCOW_HOSTNAME, and a correct reverse zone PTR pointing to this domain. - root access or a user with sudo privileges.
Environment variables
SERVER_IP— the external IP address of the server on which Mailcow runs.MAILCOW_HOSTNAME— the fully qualified domain name that will be used as the main host of the mail service.MAILCOW_TIMEZONE— the server time zone (for example,Europe/Kyiv), required for correct logging and scheduling.ADMIN_EMAIL— the administrator’s email where notifications and reports will be sent.BACKUP_DIR— the directory for storing backups (a separate disk or network storage is recommended).
Installing dependencies
Install the recommended dependencies:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y git openssl curl gawk coreutils grep jq
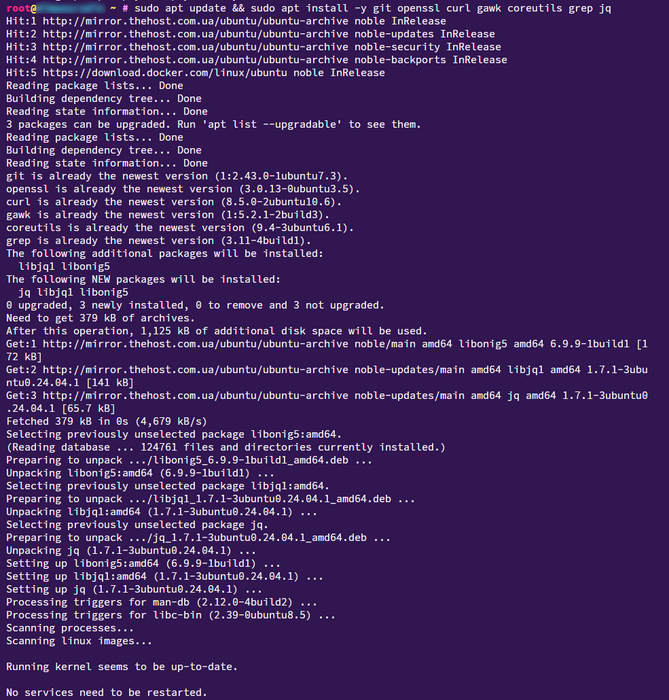
Installing Docker and Compose
See the full guide in our article: Docker and Docker Compose
Minimum required versions: Docker >= 24.0.0, Docker Compose >= 2.0. Check:
docker --version
docker compose version
If the versions are lower, update Docker/Compose according to the guide above before proceeding.
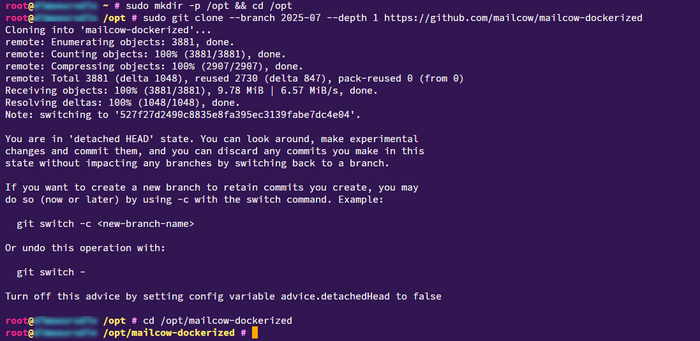
Cloning the Mailcow repository
Fetch the current Mailcow code from the official GitHub repository to deploy the mail stack in the latest stable version.
sudo mkdir -p /opt && cd /opt
sudo git clone https://github.com/mailcow/mailcow-dockerized
cd /opt/mailcow-dockerized
Generating the configuration
Run the script to generate the initial configuration:
./generate_config.sh
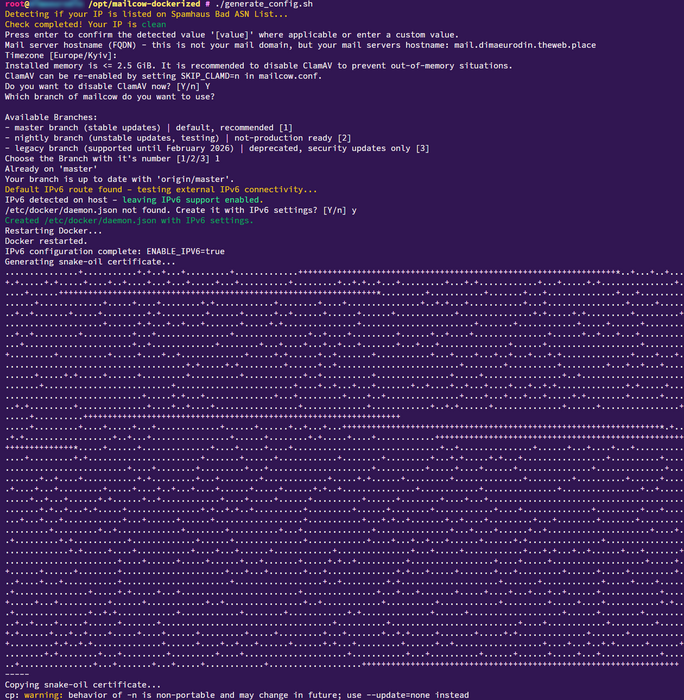
Specify:
- Mail server hostname (FQDN): enter
MAILCOW_HOSTNAME(for example,mail.example.com). - Timezone:
MAILCOW_TIMEZONE(for example,Europe/Kyiv).
The script will create mailcow.conf, where you can, if necessary, configure ports and additional SAN/server names.
Tip: if you need to make manual edits to the MailCow configuration file, run the command:
nano /opt/mailcow-dockerized/mailcow.conf
Opening ports in the firewall
Allow the mail and web ports.
sudo ufw allow 25,80,110,143,443,465,587,993,995,4190/tcp
sudo ufw reload
sudo ufw status numbered

sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 25,80,110,143,443,465,587,993,995,4190 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
Configuring DNS records
For correct mail operation you will need to configure DNS records for your MAILCOW_HOSTNAME domain. You can find more details in our guide.
Starting the containers
Start the containers and pull the required images:
docker compose pull
docker compose up -d
After startup, open https://MAILCOW_HOSTNAME/admin and log in with username admin, password moohoo. Change the administrator password immediately.
After completing the steps above, you will land in the administrative panel:
Checking ports/availability
Make sure the required ports are listening and reachable from the outside (especially 25, 80, 443, 587, 993, 995, 110, 143, 4190):
ss -tlpn | grep -E -w '25|80|110|143|443|465|587|993|995|4190'
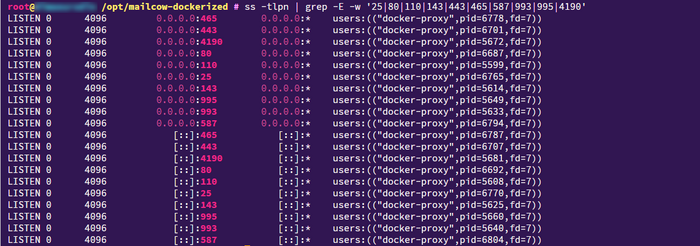
Quick breakdown of ss -lntp columns
- LISTEN — the socket is waiting for incoming connections
- Local Address:Port — where exactly the port is “bound”
- 0.0.0.0:PORT — listening on all IPv4 interfaces
- [::]:PORT or *:PORT — listening on all IPv6
- 127.0.0.1:PORT — available locally only
- users:(… pid=…) — which process holds the port (name and PID).
Service configuration
Adding a domain name
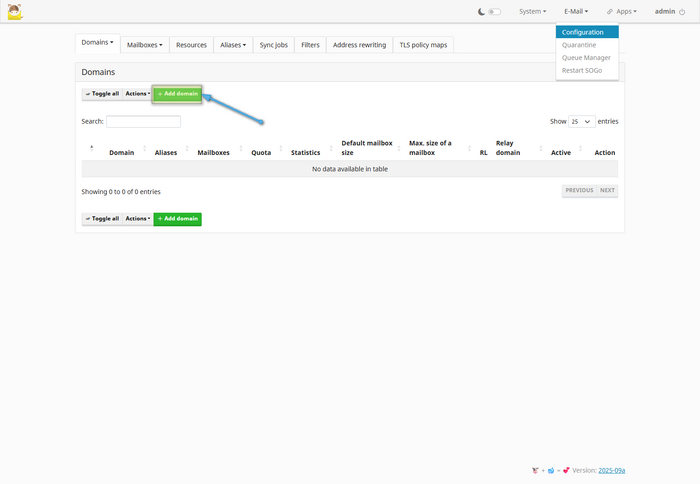
Create a domain and set it as the primary one for receiving and sending mail. After adding, the system will automatically offer to generate a DKIM key and will suggest the necessary DNS records for correct operation (MX, SPF, DKIM, DMARC).
To do this, go to E-mail → Configuration → Add domain
Configuring additional features
Reverse proxy (Nginx/Traefik)
- Bind the Mailcow web interface to
127.0.0.1viaHTTP_BIND/HTTPS_BIND, and publish it externally through the proxy. - If you use an interface domain different from
MAILCOW_HOSTNAME, fill inADDITIONAL_SERVER_NAMES(comma-separated, no spaces) and only then restart the stack.
docker compose down && docker compose up -d
SSL and Let’s Encrypt
By default the built-in ACME container will issue a certificate for MAILCOW_HOSTNAME and names from ADDITIONAL_SAN. To force certificate renewal, restart the ACME container:
docker compose restart acme-mailcow
Tip: to issue the certificate correctly, make sure port 80/TCP is open.
Backups and restore
Mailcow provides the helper-scripts/backup_and_restore.sh script for backup/restore.
Run the specified command from the root of the MailCow project(/opt/mailcow-dockerized).
# Backup of all components with deletion of backups older than 14 days
sudo ./helper-scripts/backup_and_restore.sh backup all --delete-days 14 --target BACKUP_DIR
# Restore from the directory with backups
sudo ./helper-scripts/backup_and_restore.sh restore --target BACKUP_DIR
Schedule cron jobs and check the backup execution logs.
Security
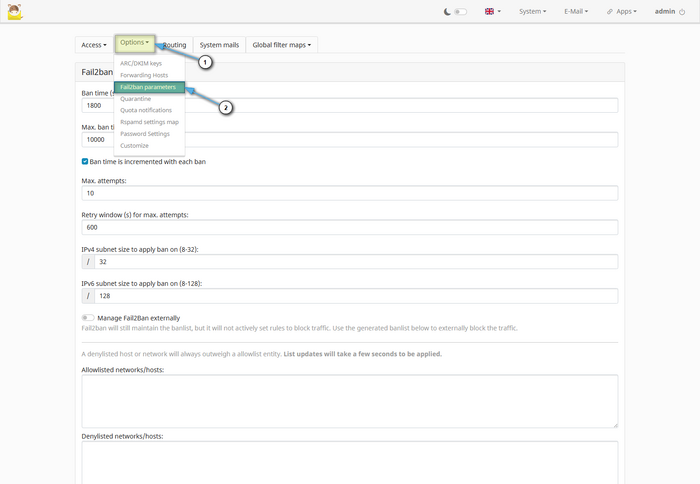
Manage ban policies in Fail2Ban by going to System and selecting Configuration.
In the window that opens, select Options and open the Fail2Ban parameters section.
Updates
To perform updates in the project directory, run:
./update.sh
Common errors
| Error / Symptom | Cause | Solution | Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACME does not issue/renew the certificate | Port 80 is closed or incorrect ADDITIONAL_SAN/proxy settings |
Open 80/TCP, adjust SAN/proxy and restart acme-mailcow |
docker compose logs -f acme-mailcow |
| No incoming mail | 25/TCP is closed from outside or filtered by the provider | Open 25/TCP; if blocked by the provider, use a suitable VPS | telnet <SERVER_IP> 25 from an external network |
| Conflict 80/443 | A web server is already listening on the host | Use a reverse proxy, bind Mailcow to 127.0.0.1 | ss -tlpn grep -E '80 / 443' |
| Incorrect HTTP(S) bindings | The IP:PORT format was used for HTTP/HTTPS |
Use HTTP_PORT/HTTPS_PORT and HTTP_BIND/HTTPS_BIND separately |
Check mailcow.conf |
Port error in Compose (:443:443) |
Incorrect port publishing syntax | Specify the correct port value without an empty : prefix |
Validate with docker compose config |
| Cannot log in to the panel after update | Login routes changed in 2025-03 | Use https://<HOST>/admin for the administrator |
Check the release notes |
Useful links
Official documentation