6.21 Issuing SSL Certificates Using Certbot

SSL Certificate is essential for protecting your website via HTTPS. It encrypts traffic between the user and the server, increases trust, and contributes to better SEO rankings. One of the easiest ways to get a free certificate is by using Certbot from Let’s Encrypt.
This guide explains how to issue and install an SSL certificate on your VPS or dedicated server using Certbot.
Important: If your website is hosted using our shared hosting or on a server with ISPManager4, this guide does not apply to you. Those platforms already have a built-in, faster way to enable Let’s Encrypt SSL. You can find the current instructions here.
Requirements
Before starting, make sure:
- You have a domain name pointing to your server (via an A record).
- Your server is running an up-to-date Linux OS.
- A web server like Nginx or Apache is installed.
- Ports 80 and 443 are open.
Note: Let’s Encrypt certificates are valid for 90 days. However, Certbot can automatically handle renewals.
Step-by-Step Certbot Installation
Note: These commands are for Ubuntu 22.04. On CentOS, use sudo yum instead of sudo apt.
1. Update system packages:
sudo apt update
2. Install Certbot and the plugin for your web server:
For Nginx
sudo apt install -y certbot python3-certbot-nginx
For Apache
sudo apt install -y certbot python3-certbot-apache
3. Check Certbot version:
certbot --version

If you see an up-to-date version (e.g. certbot 1.32.0), you’re good to go.
Issuing the Certificate
1. Make sure your site is accessible over HTTP. Open your domain (e.g. example.com) in a browser. Certbot verifies domain ownership via port 80.
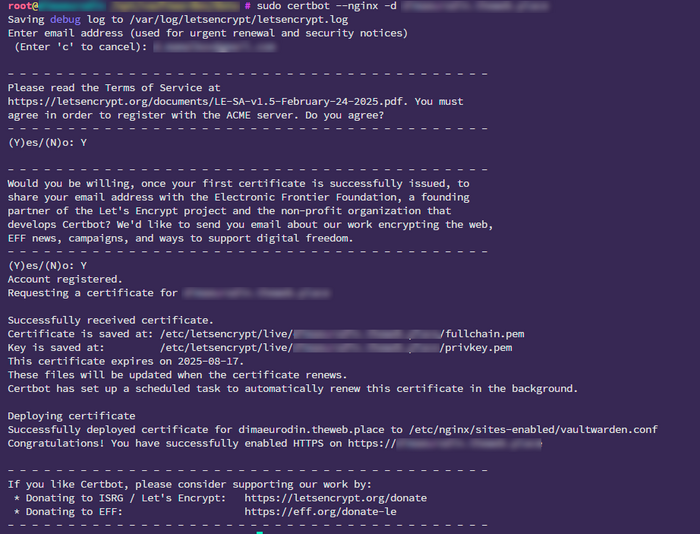
2. Run Certbot:
For Nginx
sudo certbot --nginx
For Apache
sudo certbot --apache
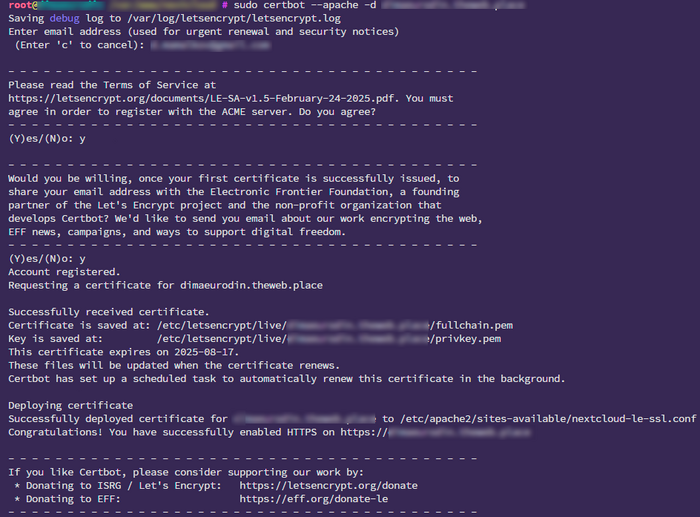
During setup, Certbot will:
- Detect your virtual hosts
- Let you choose the domain
- Automatically configure HTTPS
Tip: Certbot will also modify your Nginx/Apache config to add an HTTPS redirect.
3. Test your setup. Open your website in a browser — if everything works, you’ll see a padlock icon and the https:// prefix.
You can also test via CLI:
curl -I https://example.com
Automatic Renewal
Certbot installs a cron job or systemd-timer for automatic certificate renewal.
To test renewal manually:
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If you see Congratulations, all renewals succeeded, everything is working properly.
Summary
Your site is now protected with a free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt, and Certbot will automatically renew it.
What’s next?
- Manually configure a redirect from HTTP to HTTPS if you skipped this in Certbot.
- Add HSTS headers to your web server config.
- Set up CloudFlare with SSL.